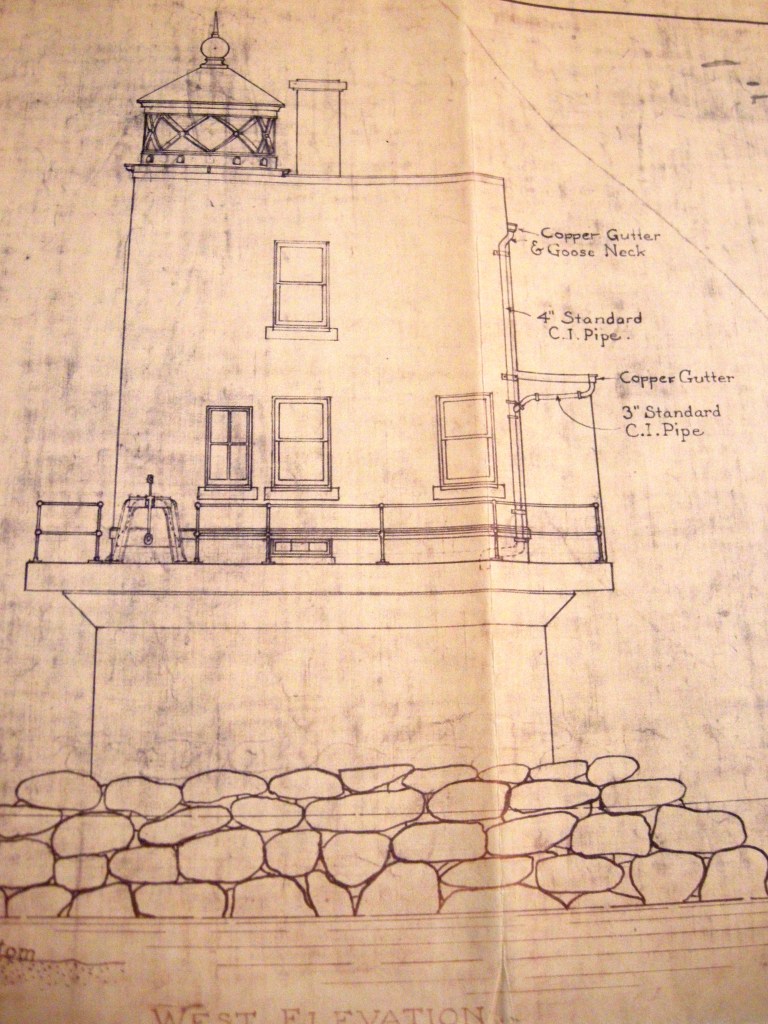
Muscle Shoal Bed (Lost to Time)
Some of our Portsmouth stories come from research into items in the Portsmouth Historical Society collection. In researching our Civil War Sword, we rediscovered another item in the collection. We have the blueprints of the last Mussel Shoal Lighthouse. Musselbed Shoals is a dangerous spot for navigation through the channel from Narragansett Bay to Mount Hope Bay. It is even noted on colonial era maps. In 1871 a beacon was placed there followed by a new light in 1873. This structure was damaged by ice floes. A new structure with built with more protection, but ice floes in 1919 -1920 damaged this one as well. The light was abandoned in 1938 and the lighthouse was severely damaged by the Hurricane of 1938. Later the building was torn down and an automatic light was installed that remains today.
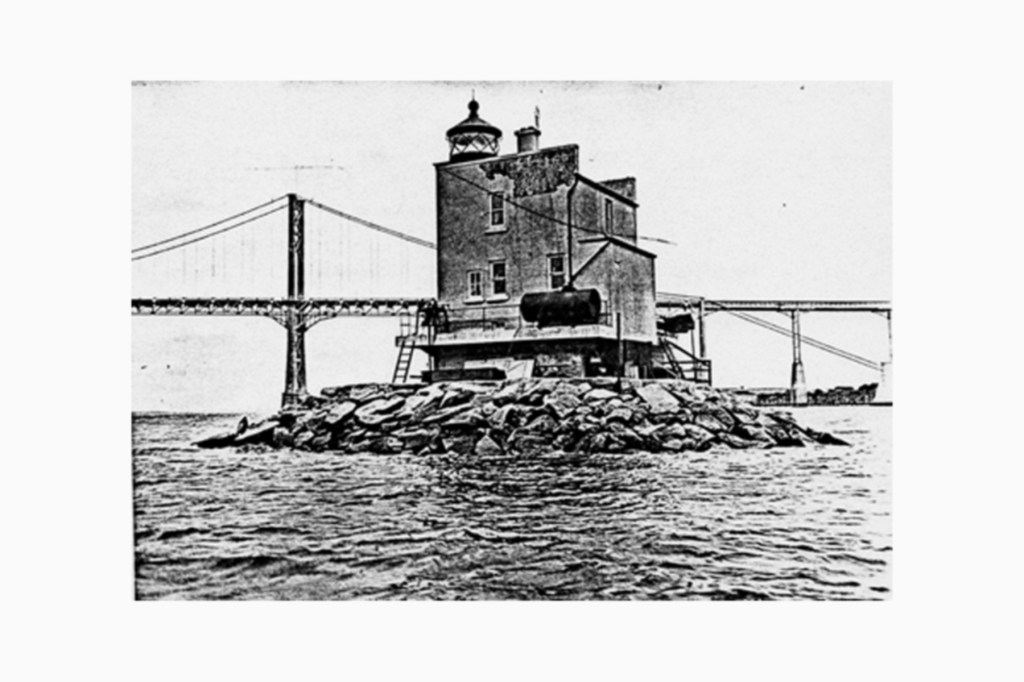

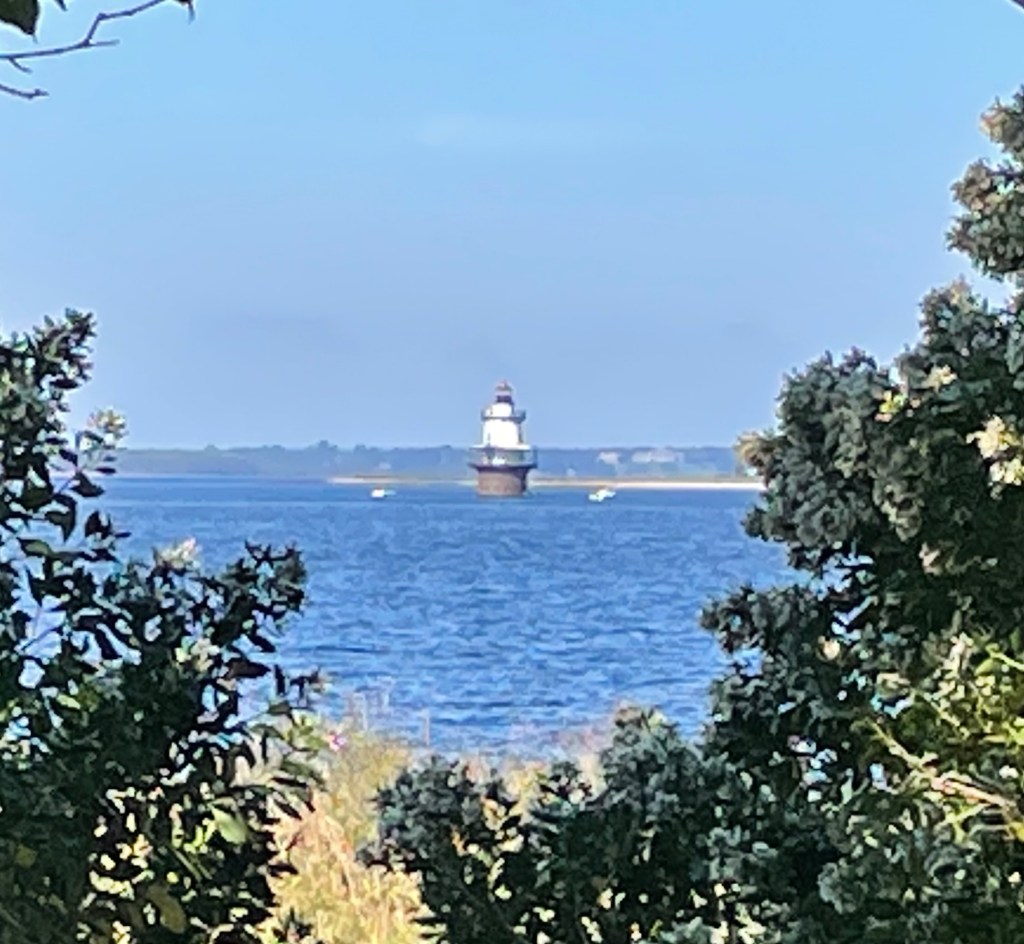
Hog Island Light
Treacherous shoals are marked by this 1901 lighthouse near Hog Island. There was a small light boat on the spot that the Old Colony Steamship Company used to aid their vessels. A larger boat, the Eel Grass Shoal Lightship, LV 12, was used beginning in 1886. The lighthouse is part of the category of “sparkplug” lighthouses, whose superstructure rests on concrete. This was the last light station established in the state. It was automated in 1964. In 1988 it was added to the National Register of Historic Places In 2006 the lighthouse was auctioned off and bought by a private buyer.
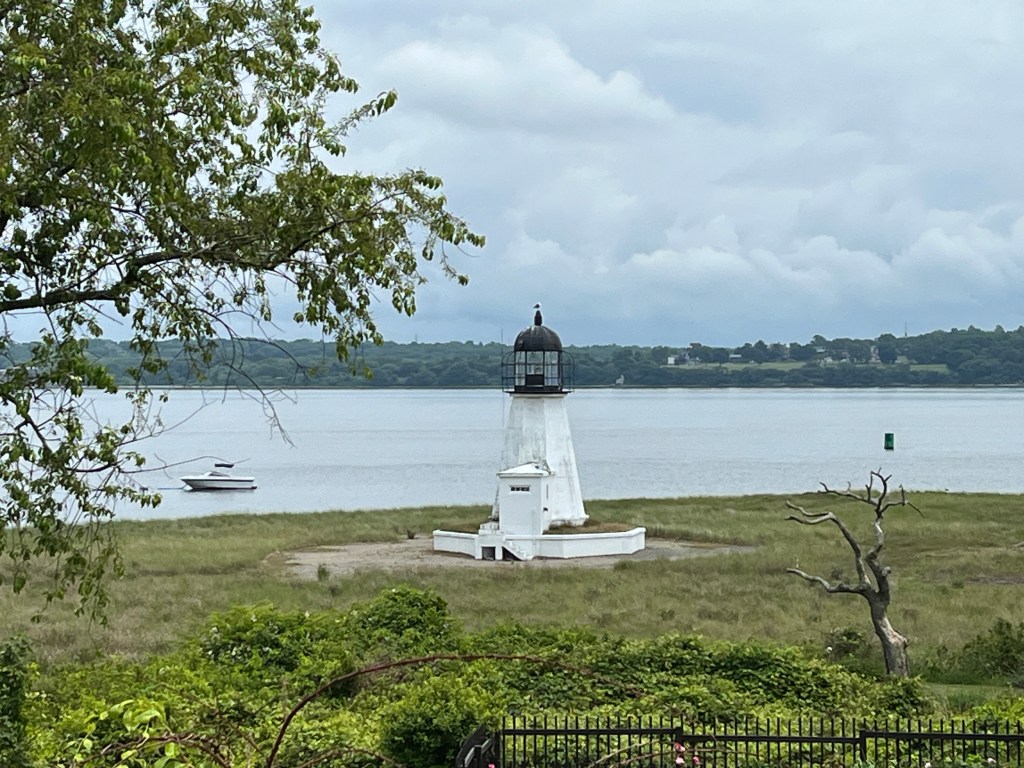
Sandy Point Light – Prudence Island
The Prudence Island Lighthouse is also known as the Sandy Point Lighthouse. It is the oldest lighthouse in the state and was originally built in 1823 by Goat Island. The Newport Harbor Light is on the spot now. In 1851 it was moved to Prudence Island. It is one of the few lighthouses with a “bird cage” structure for the lantern. The keeper’s house was swept away in the 1938 Hurricane and five people were washed out to sea and drowned.